Process
A process is a program in execution. For example, when we write a program in C or C++ and compile it, the compiler creates a binary code. The original code and Binary code, both are programs. When we actually run the binary code, it becomes a process.
Program vs Process


A process is a program in execution. For example, when we write a program in C or C++ and compile it, the compiler creates a binary code. The original code and Binary code, both are programs. When we actually run the binary code, it becomes a process.
Program vs Process
process is program under execution ,process is an active entity
while a program is in form of programming language and program is a passive entity.
moreover,a program is stored in secondary storage but process is stored in memory
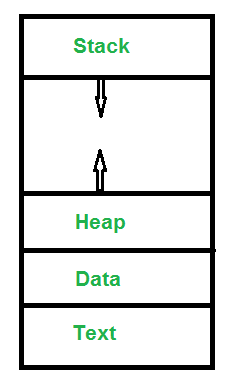
What does a process look like in Memory?
Text Section:A Process is also sometimes known as the Text Section. It also includes the current activity represented by the value of Program Counter.
Stack: Stack contains the temporary data such as function parameters, returns address and local variables.
Data Section: Contains the global variable.
Heap Section: Dynamically allocated memory to process during its run time.
Stack: Stack contains the temporary data such as function parameters, returns address and local variables.
Data Section: Contains the global variable.
Heap Section: Dynamically allocated memory to process during its run time.
Attributes or Characteristics of a Process
A process has following Attributes.
A process has following Attributes.
1. Process Id: A unique identifier assigned by operating system
2. Process State: Can be ready, running, .. etc
3. CPU registers: Like Program Counter (CPU registers must be saved and
restored when a process is swapped out and in of CPU)
5. Accounts information:This includes the amount of CPU used for process execution,time limits, execution ID etc.
6. I/O status information: For example devices allocated to process,
open files, etc
8. CPU scheduling information: For example Priority (Different processes
may have different priorities, for example
a short process may be assigned a low priority
in the shortest job first scheduling)
All the above attributes of a process are also known as Context of the process.
Every Process has its known Program control Block(PCB) i.e each process will have a unique PCB. All the Above Attributes are the part of the PCB.
Every Process has its known Program control Block(PCB) i.e each process will have a unique PCB. All the Above Attributes are the part of the PCB.
Mode switching
A user process undergoes a mode switch when it needs access to system resources. This is implemented through the system call interface or by interrupts such as page faults.
There are two modes:
- User mode
- Kernel mode
Processor time spent in user mode (application and shared libraries) is reflected as user time in the output of commands such as the vmstat, iostat, and sar commands. Processor time spent in kernel mode is reflected as system time in the output of these commands.
Comments
Post a Comment