1. What is short, long and medium-term scheduling?
Long-term scheduler: determines which programs are admitted to the system for processing. It controls the degree of multiprogramming. Once admitted, a job becomes a process.
Medium term scheduling is part of the swapping function. This relates to processes that are in a blocked or suspended state. They are swapped out of real-memory until they are ready to execute. The swapping-in decision is based on memory-management criteria.
Short term scheduler, also know as a dispatcher executes most frequently, and makes the finest-grained decision of which process should execute next. This scheduler is invoked whenever an event occurs. It may lead to interruption of one process by preemption.
2. What is deadlock? What are the necessary conditions for deadlock?
Deadlock is a situation when two or more processes wait for each other to finish and none of them ever finish.
Consider an example when two trains are coming toward each other on same track and there is only one track, none of the trains can move once they are in front of each other.
Similar situation occurs in operating systems when there are two or more processes hold some resources and wait for resources held by other(s).
Necessary conditions for deadlock:
Mutual Exclusion: There is s resource that cannot be shared.
Hold and Wait: A process is holding at least one resource and waiting for another resource which is with some other process.
No Preemption: The operating system is not allowed to take a resource back from a process until process gives it back.
Circular Wait: A set of processes are waiting for each other in circular form.
3. Virtual memory (also virtual storage) is a memory management technique. which "creates the illusion to users of a very large (main) memory."
Virtual memory creates an illusion that each user has one or more contiguous address spaces, each beginning at address zero. The sizes of such virtual address spaces is generally very high.
The idea of virtual memory is to use disk space to extend the RAM. Running processes don’t need to care whether the memory is from RAM or disk. The illusion of such a large amount of memory is created by subdividing the virtual memory into smaller pieces, which can be loaded into physical memory whenever they are needed by a process.
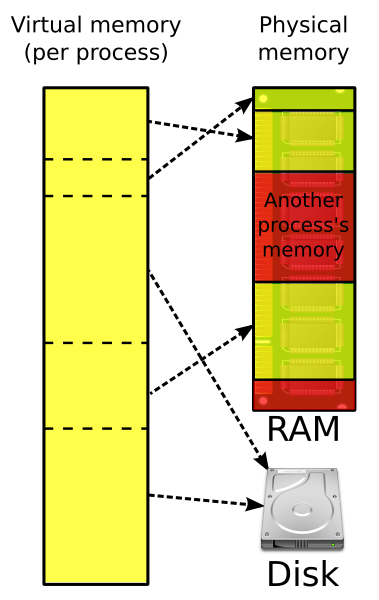
Virtual memory is commonly implemented by demand paging. It can also be implemented in a segmentation system. Demand segmentation can also be used to provide virtual memory.
4.
Comments
Post a Comment